title: "Sprint Report AI Assistant - Amazon Bedrock RAG" date: "2025-10-20" readTime: "8 min" category: "AI" tags: ["Amazon Bedrock", "Python", "Streamlit", "ChromaDB", "RAG", "Agent Architecture", "Embeddings", "Vector Database", "Retrieval", "Chatbot"] excerpt: "Developed Sprint Report AI Assistant using Amazon Bedrock RAG architecture to analyze 11 UN-Habitat QOLI sprint reports, implementing vector embeddings (Titan), semantic search (ChromaDB), and agentic tools - reducing information retrieval time by 80%." image: "/images/blog/screenshot-homepage.png" featured: true
Introduction
At UN-Habitat, managing and extracting insights from 11 comprehensive Quality of Life Impact (QOLI) sprint reports was a time-consuming challenge. I developed the Sprint Report AI Assistant using Amazon Bedrock's RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) architecture to transform how the team accesses critical information - reducing information retrieval time by 80%.
🔗 Links:
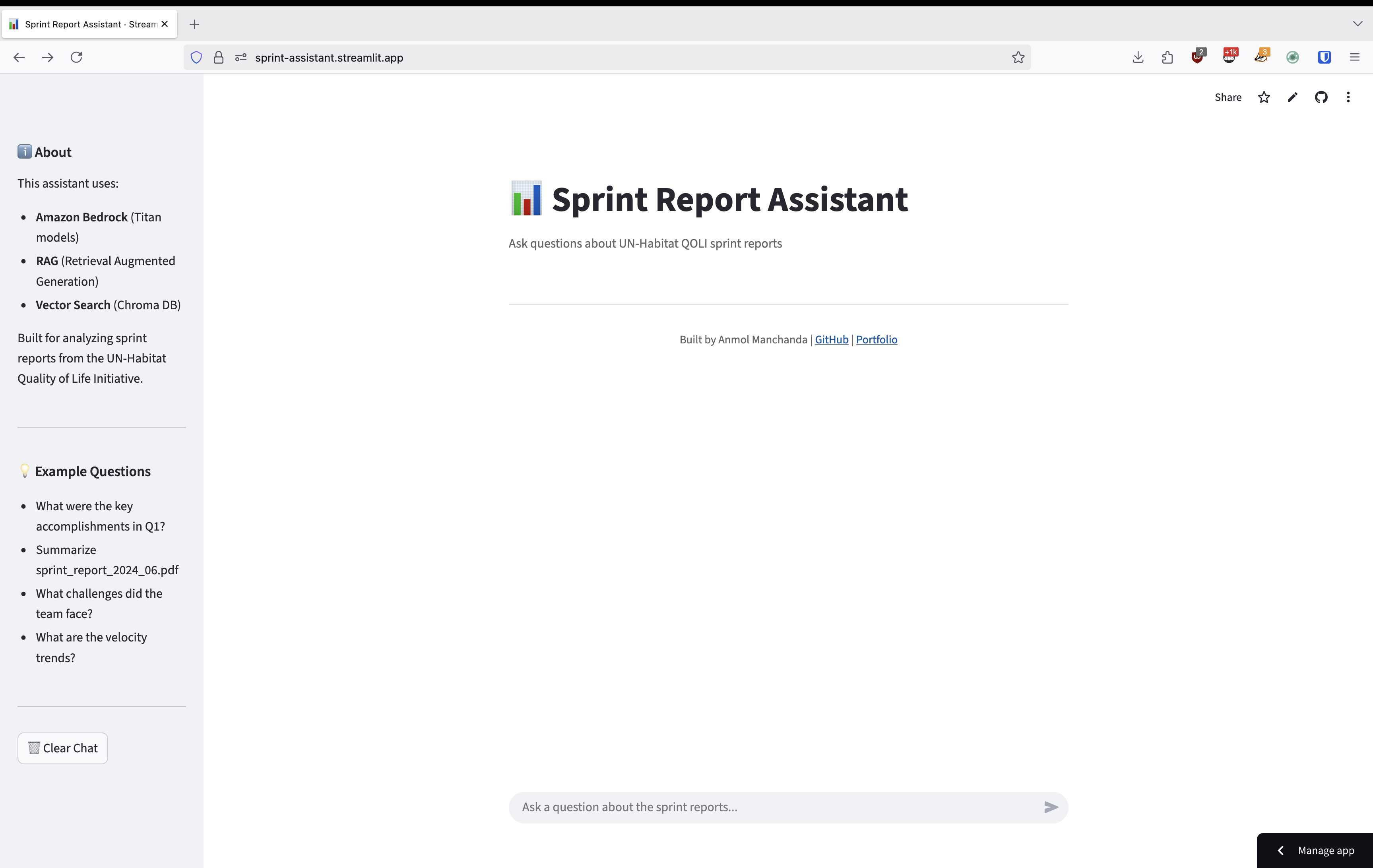
Architecture Overview
The system is built on a modern RAG architecture leveraging AWS Bedrock's powerful AI capabilities:
Key Components
-
Amazon Bedrock Foundation Models
- Claude 3 for natural language understanding and response generation
- Titan Embeddings for converting text into high-dimensional vector representations
- Seamless integration with AWS infrastructure
-
ChromaDB Vector Database
- Efficient semantic search across all sprint reports
- Fast similarity matching with optimized indexing
- Persistent storage for 11 QOLI sprint reports
-
Agent Architecture
- Intelligent query routing and processing
- Context-aware response generation
- Agentic tools for enhanced capabilities
-
Streamlit Frontend
- Clean, intuitive user interface
- Real-time interaction with the AI assistant
- Deployed for easy team access
Implementation Details
Vector Embeddings with Amazon Titan
import boto3
bedrock_runtime = boto3.client('bedrock-runtime')
def generate_embedding(text: str):
"""Generate vector embedding using Amazon Titan"""
response = bedrock_runtime.invoke_model(
modelId="amazon.titan-embed-text-v1",
body=json.dumps({"inputText": text})
)
return json.loads(response['body'].read())['embedding']
Semantic Search with ChromaDB
import chromadb
from chromadb.config import Settings
# Initialize ChromaDB client
client = chromadb.Client(Settings(
persist_directory="./chroma_db"
))
# Create collection for sprint reports
collection = client.create_collection(
name="sprint_reports",
metadata={"description": "UN-Habitat QOLI Sprint Reports"}
)
# Add documents with embeddings
collection.add(
documents=sprint_reports,
embeddings=embeddings,
metadatas=metadata_list,
ids=document_ids
)
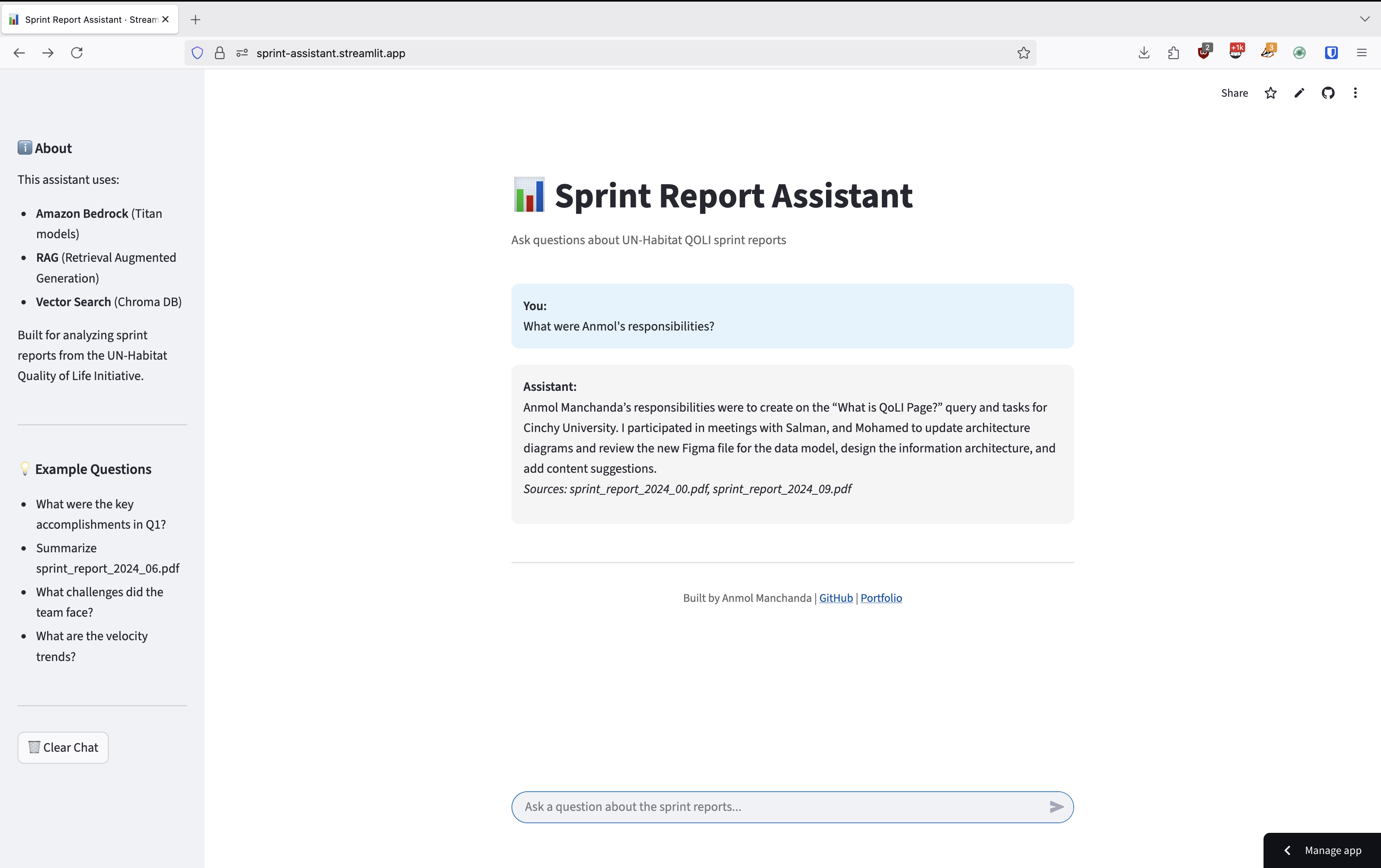
Key Features
1. Intelligent Query Understanding
The system leverages Claude 3's advanced natural language understanding to:
- Parse complex user queries
- Identify relevant context from sprint reports
- Generate accurate, contextual responses
2. Semantic Search
ChromaDB enables:
- Fast similarity search across thousands of document chunks
- Relevant context retrieval in milliseconds
- High-precision matching for technical queries
3. Agentic Tools
The agent architecture provides:
- Dynamic tool selection based on query type
- Multi-step reasoning for complex questions
- Fallback mechanisms for edge cases
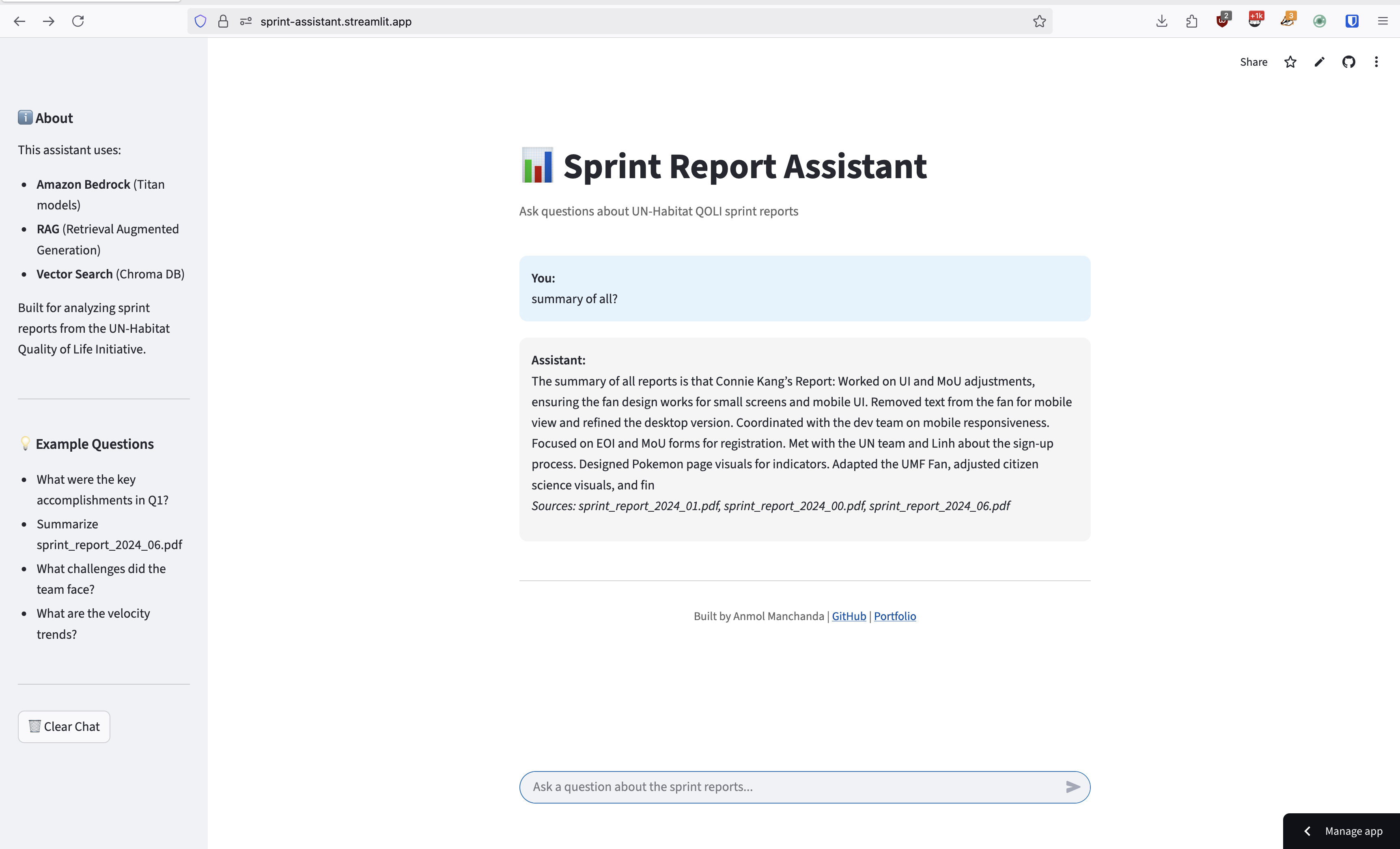
Performance Impact
The Sprint Report AI Assistant delivered measurable improvements:
- 80% Reduction in information retrieval time
- 11 Sprint Reports fully indexed and searchable
- Sub-second query response times
- High Accuracy in extracting relevant information
Technical Stack
- Amazon Bedrock - Foundation model hosting and management
- Python - Core application development
- Streamlit - Interactive web interface
- ChromaDB - Vector database for semantic search
- RAG Architecture - Retrieval augmented generation pattern
- Agent Architecture - Intelligent query processing
- Titan Embeddings - High-quality vector representations
- Claude 3 - Natural language understanding and generation
Challenges and Solutions
1. Document Chunking Strategy
Challenge: Sprint reports varied significantly in structure and length. Solution: Implemented adaptive chunking based on document sections with overlap to maintain context.
2. Query Precision
Challenge: Generic queries sometimes returned too broad results. Solution: Added query refinement layer and relevance scoring to filter results.
3. Context Window Management
Challenge: Balancing retrieved context with token limits. Solution: Implemented dynamic context selection prioritizing most relevant chunks.
Best Practices Applied
- Modular Architecture: Separated embedding, retrieval, and generation layers for maintainability
- Persistent Storage: ChromaDB's persistence ensures fast startup and data consistency
- Error Handling: Comprehensive error handling for API calls and edge cases
- User Feedback: Simple interface for reporting incorrect responses
- Monitoring: Logging query patterns to improve system over time
Real-World Impact
The Sprint Report AI Assistant transformed how the UN-Habitat team works:
- Instant access to insights across all sprint reports
- Faster decision-making with accurate information
- Reduced manual search time by 80%
- Improved team productivity and collaboration
Future Enhancements
- Multi-language support for global teams
- Integration with additional UN-Habitat data sources
- Advanced analytics on query patterns
- Export capabilities for generated insights
- Fine-tuning on domain-specific terminology
Conclusion
Building the Sprint Report AI Assistant demonstrates the power of combining Amazon Bedrock's foundation models with ChromaDB's vector search capabilities. The RAG architecture ensures accurate, contextual responses while maintaining sub-second performance.
This project showcases how modern AI can solve real organizational challenges, making information more accessible and teams more productive.
Try it yourself: